Portal:Sharks
Welcome to the shark portal

Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorpha (or Selachii) and are the sister group to the Batoidea (rays and kin). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as Cladoselache and Doliodus first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The oldest confirmed modern sharks (selachimorphs) are known from the Early Jurassic, about 200 million years ago, though records of true sharks may extend back as far as the Permian.
Sharks range in size from the small dwarf lanternshark (Etmopterus perryi), a deep sea species that is only 17 centimetres (6.7 in) in length, to the whale shark (Rhincodon typus), the largest fish in the world, which reaches approximately 12 metres (40 ft) in length. They are found in all seas and are common to depths up to 2,000 metres (6,600 ft). They generally do not live in freshwater, although there are a few known exceptions, such as the bull shark and the river shark, which can be found in both seawater and freshwater. Sharks have a covering of dermal denticles that protects their skin from damage and parasites in addition to improving their fluid dynamics. They have numerous sets of replaceable teeth.
Several species are apex predators, which are organisms that are at the top of their food chain. Select examples include the tiger shark, blue shark, great white shark, mako shark, thresher shark, and hammerhead shark. (Full article...)
Selected article -
This shark is an active, fast-swimming predator that is capable of maintaining a higher body temperature than the surrounding sea water. Its long tail is used in a whip-like fashion to stun its prey, mostly small schooling forage fish. Like other mackerel sharks, it has an ovoviviparous mode of reproduction and gives birth to live young. The common thresher is commercially important in many parts of the world: the meat and fins are sold for human consumption, the skin is made into leather, and the liver oil is processed for vitamins. This species is also valued by recreational anglers as it is an exceptionally strong fighter on hook-and-line. As a result of increasing exploitation, the common thresher was assessed as Vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) in 2007.
Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that Hixxy and Sharkey created a schism in the UK rave music scene in 1995?
- ... that the ampullae of Lorenzini enable sharks to sense electric fields?
- ... that Timo Meier became the first player in San Jose Sharks franchise history to score five goals in one game when he was 25?
- ... that "the Hurricane Shark is real"?
- ... that Alexis Sharkey's last Instagram post before her murder documented her travels to Tulum, Mexico?
- ... that since 2018, IKEA's stuffed toy shark Blåhaj has become a popular Internet meme and an icon of the online transgender community?
Categories
Related portals
WikiProjects
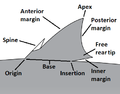
Selected picture -

More Did you know? -
- ... that no more than 250 mature northern river sharks are estimated to live in the wild?
- ... that the closure of the Tethys Sea 10–14 million years ago led to the sicklefin lemon shark and the lemon shark becoming separate species?
- ... that the spined pygmy shark, dwarf lanternshark and pygmy ribbontail catshark are candidates for being the smallest shark in the world, all maturing at under 20 cm (8 in) long?
- ... that most attacks on humans by the blacktip reef shark consist of people being bitten on their legs or feet while wading in shallow water?
- ... that the egg capsule of the crested bullhead shark has paired tendrils extending up to 2 m (6.6 ft), greater than the length of the adult shark?
General images
Topics
For additional lists of marine life-related featured articles and good articles see:
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus